Silvafeed® Nutri P: the right solution to prevent and treat diarrheal diseases
Gastrointestinal disorders remain a challenge to control and can severely affect the health and welfare of different animal species. Yet, plants produce an impressive array of compounds which can potentially be used as natural solutions to improve gut health.
Tannins are widely spread in the plant kingdom and they are certainly an element of interest in this sense. Thanks to their antibacterial, antiviral or antispasmodic properties (Lupini et al., 2009), they have been traditionally used within ethnoveterinary medicine to treat various illnesses affecting monogastrics, such as diarrhea and other intestinal disorders (Palombo, 2006; Suroowan et al., 2017).
Silvateam is recognised as a world leading player in tannins and,in the last decades, it has been strongly investigating tannin health benefits within animal nutrition.
Silvafeed® Nutri P is a feed additive composed of natural polyphenols (mainly hydrolysable tannins), which have been extracted and purified from various botanical sources. Its antispasmodic effect has been deeply analysed by an ex vivo assessment carried out by Budriesi et al., in 2010. The aim of the study was to provide an evidence of Silvafeed® Nutri P antispasmodic activity, which triggers a reduction in intestinal motility and, therefore, delays gastrointestinal transit, making this extract a helpful tool to prevent or treat diarrheal diseases.
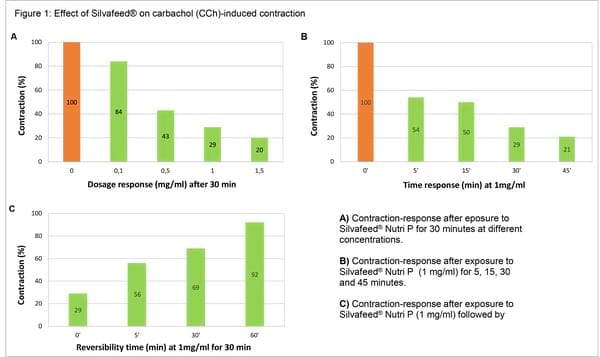
Different gut segments (ileum and proximal colon) were isolated from guinea pigs and incubated with Silvafeed® Nutri P, in order to assess its effect on the contraction (or spasm) of the smooth muscle from the intestinal wall. This mechanism was tested in a series of experiments where muscle contraction was induced by various agonists such as carbachol (CCh), BaCl2, KCl, histamine or serotonin.
As highlighted in the above chart, Silvafeed® proved its strong efficacy in reducing CCh induced muscle contraction of both gut segments. Thus, the tannins antispasmodic activity presented an impact on the different assessed parameters, which may vary in strength depending on the gut locations, either ileum or proximal colon (Figure 1).
Various beneficial effects were obtained with the other tested antagonists.
Silvafeed® Nutri P inhibitory action reached maximum efficacy at a dosage of 1 mg/ml: it was noncompetitive and completely reversible after washing the tissue for up to 60 min. The trial results also suggested that the intestinal tissues from guinea pigs were not damaged after being in contact with Silvafeed®.
Moreover, Silvafeed® Nutri P exerted other beneficial effects related to two contrasting actions in the proximal colon. Firstly, on one hand the tannins prevented the strong muscle contraction caused by the stimulation of neuronal serotonin-receptors within the gut. On the other hand, they did not interfere with the muscle relaxation caused by the direct stimulation of serotonin-receptors located in the proximal colon muscle. Therefore these results highlighted the selective inhibitory activity of Silvafeed® Nutri P.
Secondly, Silvafeed® Nutri P antispasmodic effect did not changed in the presence of probiotics such as Saccharomyces boulardii, which exert well-known benefits against various gastrointestinal disorders.
To summarise, Silvafeed® Nutri P was suitable for keeping gastrointestinal disorders under control thanks to its following properties:
* Antispasmodic effect
* Ability to relax the gut muscles without damaging the intestinal tissues
* Strong antibacterial and antiviral activities
* Synergistic efficacy with probiotics
References
Budriesi R., loan P., Micucci M., Micucci E., Limongelli V. and Chiarini A., 2010. Stop Fitan: Antispasmodic Effect of Natural Extract of Chestnut Wood in Guinea Pig Ileum and Proximal Colon Smooth Muscle. Journal of Medicinal Food, 13(5):1104-1110.
Lupini C., Cecchinato M., Scagliarini A., Graziani R. and Catelli E, 2009. In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Chestnut and Quebracho Woods Extracts against Avian Reovirus and Metapneumovirus. Research in Veterinary Science, 87:482-487.
Palombo E.A., 2006. Phytochemicals from Traditional Medicinal Plants Used in the Treatment of Diarrhoea: Modes of Action and Effects on Intestinal Function. Phytotherapy Research, 20(9):717-724.
Suroowan S., Javeed F., Ahmad M., Zafar M., Noor M.J., Kayani S., Javed A. and Mahomoodally M.F. 2017. Ethnoveterinary Health Management Practices Using Medicinal Plants in South Asia – a Review. Veterinary Research Communications, 41(2):147-168