Aquaculture Europe 2016 Edinburgh, Scotland
In Vitro Activity of Hydrolysable Tannins Against Common Fish Pathogens
Introduction
Scientific studies demonstrated a positive effect of hydrolizable tannins against the growth of certain pathogens and thus promoting health and balance of the intestinal flora. The feed additive Silvafeed TSP (Hydrolysable Tannins)declared to have protein absorption enhancement, pathogenic bacteria suppression and vasoconstriction properties in poultry and ruminant digestive tracts, has been tested in vitro to determine its antibacterial effects against bacterial fish pathogens. Among the diseases in intensive fish farming, bacteria are the most significant pathogens of cultured fish. Aeromonas hydrophila, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus iniae, Lactococcus garviase and Yersinia ruckeri are bacterial pathogens causing infectious diseases in fish (Lukkana et al., 2011). A. hydrophila is a common bacteria in freshwater habitats throughout the world and is present in normal microflora and inhabiting fish reservoirs (Cipriano, 2001; Floyd, 2009). The gram-positive cocci, Streptococcus, are pathogenic bacteria which have been reported to be responsible for severe economic losses in tilapia production caused by high mortality and poor meat quality yield (Yanong and Floyd, 2006; Floyd, 2009). Lactococcosis is an emerging pathology affecting a variety of fish species all over the world. Enteric redmouth disease (ERM, yersiniosis) is one of the most important diseases of salmonids and leads to significant economic losses (Horne, 1999). Antibiotics play an important role in the disease management of aquaculture practices. However antibiotic resistance develops readily in pathogens following antibiotic treatment. Plant tissues are rich in a wide variety of secondary metabolites such as tannins, terpenoids, alkaloids and flavonoids, which have been found to have in-vitro antimicrobial properties. Some of these plant-derived compounds seem to be promising candidates to replace AGPs (Cowan, 2009; Hernandéz, 2004). A benefit of the use of tannins as an alternative to AGPs, is the hypothetical difficulty of bacteria to develop resistance against the diverse range of molecules that contain these plant compounds.
A study was done in vitro to evaluation of the minimum inhibitor activity of Silvafeed TSP (hydrolizable tannins) against 6 of the most common fish pathogen: Lactococcosis disease (Lactococcus garviae); Yersiniosis or enteric redmouth disease (Yersinia ruckeri, Aeromonas hydrophila); Foruncolosi (Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. Salmonicida), vibriosis (Listonella anguillarum) and Coldwater streptococcosis (Vagococcus salmoninarum).
Materials and methods
Antibacterial properties of Silvafeed TSP hydrolysable tannins have been assessed through Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Method at five different dosages; 0.05 %, 0.10 %, 0.025 %, 0.40 % and 0.50 %. Throughout the study Florfenicol susceptibility disks are used for antibacterial controls against all pathogens. Each dosage level is assessed in duplicate for control purposes. Furthermore the product is diluted both in PBS (phosphate buffered saline solution) and ether using the resulting solutions as controls of one another. Prepared pathogen suspensions are planted in Mueller-Hinton agar (Merck) according to Mc Farland 0.5 standards. Bacteria are incubated at 21˚C for 24-48 hours.
Results
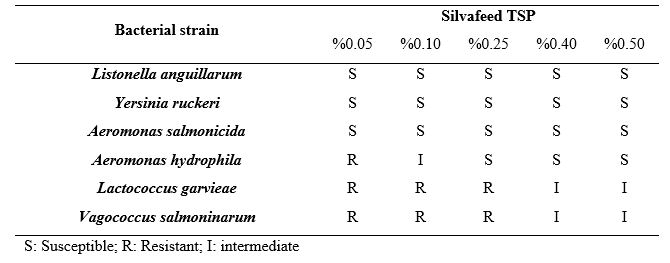
Table I shows the in vitro activity of Silvafeed TSP against Listonella anguillarum, Yersiniae ruckeri Aereomonas salmonicida supsp. Salmonicida, Aereomonas hydrophyla, Lactococcus garvieae and Vagococcus salmoninarum.
Discussion and conclusion
This in vitro study showed that Silvafeed TSP has a strong antibacterial effect against common bacterial fish pathogens as Listonella anguillarum, Yersiniae ruckeri and Aereomonas salmonicidas supsp. Salmonicida at all studied dosage levels whilst a moderate effectiveness has been observed against Aereomonas hydrophyla, and a slight effect was assessed against Lactococcus garvieae and Vagococcus salmoninarum at the higher end of the dosage range (0.40 % and 0.50 %).
The present findings indicate that hydrolysable tannin extract Silvafeed TSP is a potential antibacterial agent, Although it has a marked in vitro inhibitory effect on fish bacterial pathogens, the inhibition is necessary to be confirmed in an in vivo trial.
References
Cagirgan, H., and T. Tanrikul. “Testing the effectiveness of a Yersinia vaccine in infected and chemically treated juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).” Journal of Applied Ichthyology 14.3‐4 (1998): 239-243.
Cipriano, Rocco C., and Graham L. Bullock. Furunculosis and other diseases caused by Aeromonas salmonicida. National Fish Health Research Laboratory, 2001.
Cipriano, Rocco C., et al., 2001. Reappraisal of the federal fish health recommendation for disinfecting eggs of Atlantic salmon in iodophor. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health 13.4 : 320-327.
Cowan M.M., Plant products as antimicrobial agents, Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 12 (4) (1999) 564e582.
Floyd, Trevor A., Charles MacInnis, and Barry R. Taylor. “Effects of artificial woody structures on Atlantic salmon habitat and populations in a Nova Scotia stream.” River Research and Applications 25.3 (2009): 272-282.
Hernandez F., Madrid J., V. García, Orengo M., Megías M.D., Influence of two plant extracts on broilers performance, digestibility, and digestive organ size, Poult. Sci. 83 (2) (2004) 169e174.
Horne, M. T., and A. C. Barnes. “Enteric redmouth disease (Yersinia ruckeri).” (1999).
Lukkana, Mintra, Janenut Wongtavatchai, and Rungtip Chuanchuen. “Expression of AheABC efflux system and plasmid profile of Aeromonas hydrophila isolates from farmed nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).” The Thai Journal of Veterinary Medicine 41.4 (2011): 529.
Tanrikul, T. Tansel. “Vibriosis as an epizootic disease of rainbow trout (Onchorynchus mykiss) in Turkey.” Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences10.10 (2007): 1733-1737.
Yanong, Roy PE, and Ruth Francis-Floyd. “Streptococcal Infections of Fish1.” (2002). Cooperative Extension Service, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida.