Use of Silvafeed® Nutri P to prevent enteric disorders and boost zootechnical performances in weaned piglets
Background
Efficient natural alternatives to antibiotics and high level of zinc oxide are urgently needed for the control of post-weaning diarrhoea in piglets. Silvafeed® Nutri P (dietary tannins饲料级单宁酸) is a blend of plant extracts rich in bioactive polyphenols, which have been extensively studied for their biological properties (e.g. antispasmodic, antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory) and potential health benefits. Recently, the effectiveness of Silvafeed® plant extracts (dietary tannins饲料级单宁酸) in reducing the severity of post-weaning diarrhoea has been well described in piglets either infected (Experimental ETEC F4 model) or non-infected (Girard et al, 2018). A recent trial was conducted to evaluate the effects of Silvafeed® Nutri P (dietary tannins饲料级单宁酸) on zootechnical performances and faecal scores (consistency and colour) in weaned piglets.
Materials & Methods
108 piglets (Large White × Landrace) were weaned at 30±2 days of age, and divided into four barns (n=27). Piglets from two barns were fed a control diet (Control group). In the two other barns, piglets received the control diet supplemented with Silvafeed® Nutri P at 0.75% dosage (Silvafeed® group). The piglets were fed the different diets ad libitum from 0 to 42 days post weaning.
Growth performance and feed intake were evaluated at day 0, 14, 28 and 42. Additionally, the consistency and the colour of faeces was assessed individually for a subset of animals (n=8) according to scale scores (Rossi et al., 2012).
Results
A) Zootechnical performances
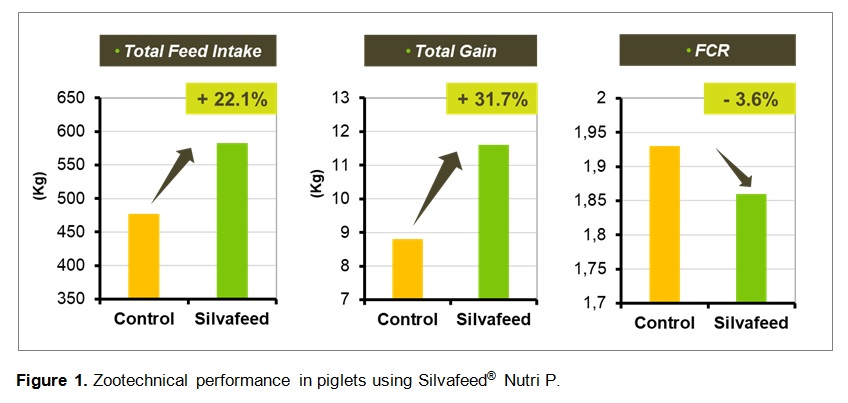
Overall, the supplementation with Silvafeed® Nutri P improved the performance of weaned piglets over 42 days period (Figure 1). Total feed intake and total gain were substantially increased in Silvafeed® group (+22.1 and 31.7% compared with control), and a reduction of feed conversion rate was also appreciable (-3.6%) compared with Control group.
The average daily gain (ADG) was constantly superior in Silvafeed® group compared with Control group for all periods (days 0?14; 15?28; 29?42; Table 1), although statistically significant difference was observed only for the last phase. In Control group, the ADG did not exceed 0.3 kg/d and was lower in the last phase (days 29?42) compared with intermediate phase (days 15?28). In comparison, the ADG in Silvafeed® group increased to over 0.3 kg/d during days 15?28 and maintained a slight increase in the last phase (days 29?42). Moreover, bodyweight of piglets remained higher in Silvafeed® group compared with Control group from day 14 onwards, with statistically significant difference found at day 42 (P<0.05; Table 1).

B) Faecal scores (consistency and colour)
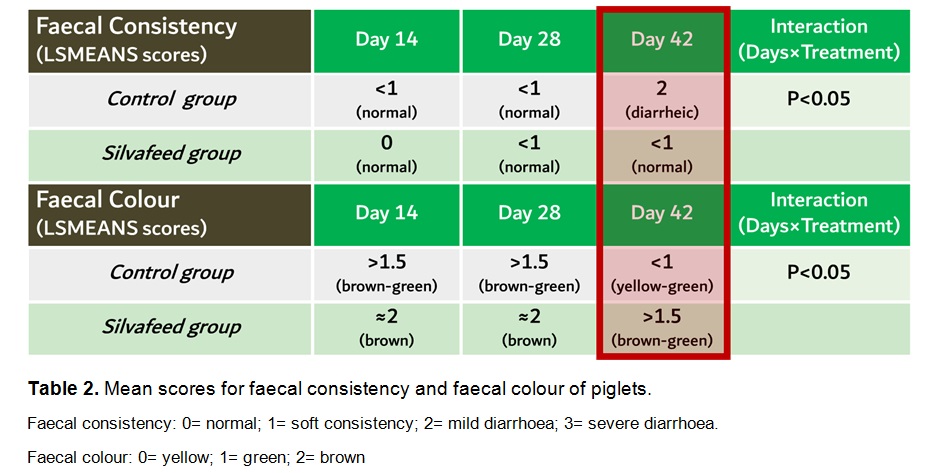
Faecal scores (consistency and colour) were also improved in Silvafeed® group compared with Control group, especially at the end of the trial in accordance with performance improvement. In fact, the mean scores in Control group at day 42 for faecal consistency and colour were 2 (diarrheic) and <1 (yellow-green) respectively. On the contrary, piglets belonging to the Silvafeed® group showed normal faecal consistency (mean score <1) and satisfying brownish faecal colour (>1.5) throughout the experiment.
Conclusion
Silvafeed® Nutri P effects have shown to improve gut health and performance of piglets during stressful post-weaning period. These promising results highlight that the use of the natural feed additive Silvafeed® Nutri P can be implemented to prevent post-weaning diarrhoea in piglets and increase significantly zootechnical performance (total gain and feed efficiency).
Authors
This article was written with the kind permission of the authors, who presented the work during the 23° Congress of the Animal Science and Production Association (ASPA), 2019, Sorrento, Italy. Poster P074: In vivo evaluation of tannin-based additives in weaned piglets.
Caprarulo V.1, Callegari M.L.2, Hejna M.1, Sotira S.1, Dell’Anno M.1, Miragoli F.2, Rossi L.1
1Dipartimento di Scienze Veterinarie per la Salute, la produzione animale e la sicurezza alimentare, Università degli Studi di Milano, Milano, Italy.
2Dipartimento di Scienze e Tecnologie Alimentari per una filiera agro-alimentare Sostenibile, Università Cattolica del S. Cuore, Piacenza, Italy.
Acknowledgements
This research study was conducted in the farm of FOODTECH PROJECT (ID 203370). This project was co-funded by European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
The authors thank ProPhos Chemical as project coordinator (Marco Michelotti), Ferraroni S.p.a. for the supply of feed and Silvateam for providing the plant-based extract Silvafeed® Nutri P.

