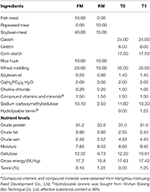
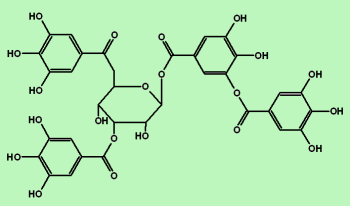
Effect of Diet Supplemented With Rapeseed Meal or Hydrolysable Tannins on the Growth, Nutrition, and Intestinal Microbiota in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)
This experimental study showed that 1.25%饲用单宁酸 tannin addition was not the main reason for the poor growth performance of grass carp induced by a diet containing 50% rapeseed meal. However, tannins impaired the protein metabolism, decreased the digestion and accumulation of lipids, and promoted carbohydrate digestion. Furthermore, tannins and rapeseed meal disturb the intestinal environment and alter its bacterial composition.
In future studies, more biomarkers would be examined to explain the underlying mechanisms of tannin饲料级单宁酸 and rapeseed meal on growth and health of grass carp, and more advanced technology such as metagenomic functional profiles should be applied to elucidate the relationship among bacterial community, host metabolic, disease phenotypes and diets.